 Nov 19, 2025
Nov 19, 2025
 Posted by Administrator
Posted by Administrator
How Aluminum Camera Shells Enhance Vehicle Cameras in Extreme Road Conditions
The Critical Role of Housing in Automotive Camera Performance
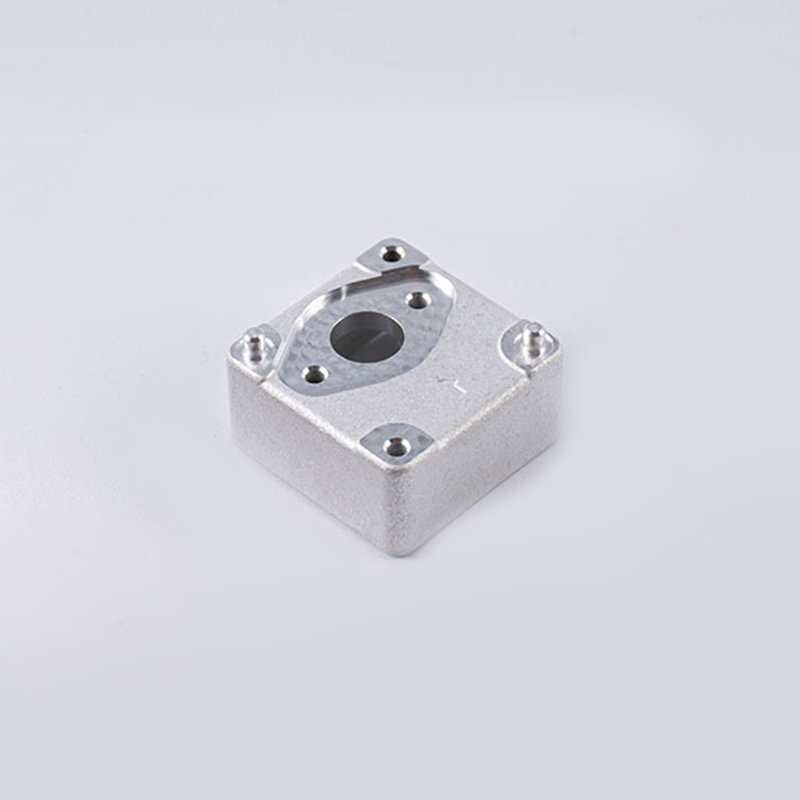
Modern vehicles increasingly rely on camera systems for safety, navigation, and documentation purposes. These visual sensors have become the electronic eyes of contemporary transportation, responsible for everything from parking assistance to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). However, the performance and longevity of these sophisticated electronic components are fundamentally dependent on their physical protection. The housing that encases camera modules serves as the first line of defense against environmental challenges, making the choice of material for these protective shells a critical engineering decision that directly impacts reliability, clarity, and durability.
Among the various materials available for camera housing construction, aluminum has emerged as a preferred choice for demanding automotive applications, particularly for vehicles that operate in challenging environments. The inherent properties of aluminum alloys offer a unique combination of benefits that address the multiple threats faced by vehicle-mounted cameras. From thermal management to impact resistance, aluminum camera housings provide performance advantages that translate to more reliable vision systems when vehicles encounter everything from extreme temperatures to rough terrain and corrosive elements.
This comprehensive examination explores the specific advantages of aluminum camera shells in protecting and enhancing vehicle camera performance under extreme road conditions. By analyzing the material properties, comparative benefits, and engineering considerations, we will demonstrate why aluminum has become the material of choice for automotive manufacturers seeking to ensure their camera systems maintain optimal performance regardless of environmental challenges.
Aluminum Camera Housing Advantages for Extreme Environments
Superior Thermal Management Properties
Vehicle cameras generate heat during operation, and when combined with external temperature extremes, this thermal load can significantly impact performance and longevity. Aluminum's exceptional thermal conductivity, approximately 50-60% that of copper but at one-third the weight, makes it uniquely suited for managing these thermal challenges. The material efficiently draws heat away from sensitive electronic components, distributing it across the housing surface where it can dissipate into the surrounding air. This passive cooling mechanism helps maintain optimal operating temperatures for image sensors and processors, preventing the thermal noise that degrades image quality in high-temperature environments.
In cold conditions, aluminum's thermal properties offer different advantages. The material responds more quickly to external temperature changes than plastics, allowing integrated heating elements (when present) to warm the internal components more efficiently. This rapid thermal response helps prevent condensation and frost formation on lens surfaces, maintaining visibility when temperatures plummet. Unlike plastic housings that can become brittle in extreme cold, aluminum maintains its structural integrity, ensuring continued protection of the camera assembly.
The following table illustrates the thermal performance comparison between aluminum and common alternative housing materials:
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (μm/m·°C) | Maximum Continuous Service Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloy 6061 | 167 | 23.6 | 250 |
| Polycarbonate Plastic | 0.2 | 70 | 115 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 16.2 | 17.2 | 925 |
| Die-Cast Zinc | 116 | 27.4 | 185 |
As the data demonstrates, aluminum offers an exceptional balance of high thermal conductivity with moderate thermal expansion, making it particularly well-suited for automotive camera applications where temperature fluctuations are frequent and extreme. The high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer away from sensitive components, while the moderate expansion coefficient reduces stress on seals and connections during temperature cycles.
Exceptional Durability and Impact Resistance
Vehicle cameras face numerous physical threats during normal operation, from road debris and vibration to accidental impacts and environmental stressors. Aluminum camera housings provide superior protection against these challenges due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and impact absorption characteristics. The inherent toughness of aluminum alloys allows for thinner wall sections that maintain structural integrity while minimizing overall weight—a critical consideration in vehicle design where unsprung mass affects handling and efficiency.
When compared to plastic housings, aluminum offers significantly better resistance to deformation under impact. While plastic may crack or shatter upon receiving a substantial impact, aluminum typically deforms in a more predictable manner, often maintaining a protective enclosure for the camera components even after significant deformation. This difference in failure mode can be crucial in preserving camera functionality after minor collisions or debris strikes. Additionally, aluminum housings better withstand the constant vibration encountered during vehicle operation, preventing fastener loosening and connection failures that can plague lesser housing materials.
The durability advantages of aluminum extend beyond immediate impact resistance. Aluminum housings maintain their protective qualities across a wide temperature range, unlike plastics that become brittle in extreme cold or may soften in high heat. This consistent performance ensures that the housing provides reliable protection whether the vehicle is operating in desert heat or arctic conditions. The material's resistance to UV degradation further enhances long-term reliability, preventing the cracking or fading that can affect plastic housings over years of sun exposure.
Specific Durability Advantages in Automotive Applications
- Superior resistance to stone chips and road debris impacts compared to plastic housings
- Maintained structural integrity across temperature extremes from -40°C to +125°C
- Excellent vibration damping characteristics that protect internal components
- Higher rigidity prevents misalignment of camera mounting and optical elements
- Better retention of fasteners and connectors compared to plastic threading
Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Conditions
Modern aluminum alloys developed for automotive applications offer exceptional corrosion resistance through both inherent material properties and advanced surface treatments. The natural formation of a protective oxide layer provides a barrier against environmental attacks, while additional anodizing or coating processes can further enhance this resistance for specific challenging environments. This corrosion protection is particularly valuable for vehicle cameras mounted in exposed locations where they encounter road salts, industrial pollutants, or marine atmospheres.
Different aluminum alloys offer varying levels of corrosion resistance, allowing engineers to select the optimal material for specific application requirements. For instance, aluminum-magnesium alloys demonstrate excellent resistance to marine environments, while aluminum-silicon alloys perform well in industrial atmospheres. This selectivity enables manufacturers to tailor the housing material to the expected operating environment, ensuring long-term reliability regardless of climate or geographic location.
When considering benefits of aluminum housing for automotive cameras in corrosive environments, several factors distinguish aluminum from alternative materials. Unlike steel, aluminum does not undergo progressive rusting that can compromise structural integrity. Unlike many plastics, aluminum does not degrade from UV exposure or become brittle from ozone attack. This balanced resistance to multiple environmental threats makes aluminum particularly well-suited for the complex chemical challenges faced by vehicle exteriors.
Addressing Common Concerns with Aluminum Camera Housings
Weight Considerations and Design Optimization
While aluminum is denser than plastic, advanced engineering and design techniques have minimized the weight penalty associated with aluminum camera housings. Through strategic use of thin-wall casting, ribbed structures, and topological optimization, manufacturers can produce aluminum housings that offer superior protection with minimal weight addition. The high strength-to-weight ratio of aluminum means that less material is required to achieve the same structural integrity as thicker plastic housings, partially offsetting the density difference.
When evaluating the overall impact on vehicle performance, the minimal weight of camera housings—typically measuring just grams—represents an insignificant fraction of total vehicle mass. The benefits of improved durability, thermal management, and longevity often far outweigh the minor weight consideration. For applications where every gram matters, aluminum-magnesium alloys provide even greater weight savings while maintaining the advantageous material properties of aluminum.
The following table compares key physical properties of aluminum with alternative housing materials:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Strength-to-Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | 2.7 | 276 | 68.9 | 102 |
| Polycarbonate | 1.2 | 62 | 2.4 | 52 |
| Stainless Steel 304 | 8.0 | 215 | 193 | 27 |
| Die-Cast Zinc | 6.6 | 220 | 85 | 33 |
As the comparison demonstrates, aluminum offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, surpassed only by more expensive composite materials. This combination of relatively low density with high strength makes aluminum particularly suitable for automotive applications where both performance and weight considerations are important design factors.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding Capabilities
Modern vehicles contain numerous electronic systems operating across a broad spectrum of frequencies, creating an electrically noisy environment that can interfere with sensitive camera electronics. Aluminum's natural conductivity provides inherent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, protecting the camera's internal components from external radio frequency interference that could degrade image quality or cause operational instability. This shielding function becomes increasingly important as vehicle electrification advances and wireless communication systems proliferate.
The continuous nature of aluminum housings—as opposed to the segmented construction often necessary with plastic housings—creates a Faraday cage effect that contains emissions from the camera electronics themselves. This containment prevents the camera system from interfering with other vehicle electronics, an important consideration for compliance with electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations. Proper design of seams and openings maintains this shielding effectiveness while allowing for necessary connections and lens openings.
When evaluating aluminum camera housing EMI shielding for ADAS applications, the integrity of the shielding becomes a safety-critical consideration. Advanced driver-assistance systems rely on clear, uninterrupted video signals to make split-second decisions, making protection against electromagnetic interference particularly important. Aluminum housings typically provide 60-100 dB of shielding effectiveness across the frequency range most critical for automotive electronics, significantly outperforming plastic housings even those with applied conductive coatings.
Specialized Applications and Future Developments
Performance in Extreme Temperature Environments
Vehicle cameras must maintain functionality across an enormous temperature range, from the intense heat of desert operation to the deep cold of arctic conditions. Aluminum's thermal properties and mechanical stability across this spectrum make it particularly well-suited for these challenging applications. The material maintains its structural integrity and protective qualities regardless of temperature extremes, ensuring consistent performance when alternative materials might fail.
In high-temperature environments, aluminum prevents the heat soak that can degrade image sensor performance and cause electronic component failure. The housing acts as a heat sink, drawing thermal energy away from sensitive components and dissipating it through the large surface area of the housing itself. This passive cooling can mean the difference between continued operation and thermal shutdown in demanding conditions. Specialized high-temperature aluminum alloys can extend this performance to even more extreme environments.
For those searching for information on aluminum camera enclosure for extreme temperature vehicle use, it's important to understand how aluminum addresses both high and low-temperature challenges. In cold conditions, aluminum's rapid thermal conduction allows any internally generated heat to quickly distribute throughout the housing, preventing localized cold spots that could lead to condensation or component failure. This balanced thermal performance makes aluminum housings uniquely capable of handling the wide temperature swings experienced by vehicle exteriors.
Protection Against Moisture and Environmental Contaminants
The integrity of camera housings against moisture intrusion represents one of the most critical factors in long-term reliability. Aluminum housings facilitate superior sealing through their rigidity, stability, and compatibility with high-performance gasket materials. The minimal thermal expansion of aluminum compared to plastics reduces stress on seals during temperature cycles, maintaining compression and preventing the seal degradation that leads to water ingress over time.
Advanced joining techniques, including laser welding and conductive epoxy bonding, can create nearly hermetic seals between aluminum housing components while maintaining EMI shielding effectiveness. These manufacturing advantages allow aluminum housings to consistently achieve IP6K9K and IP67 ratings that signify complete protection against dust and protection against temporary immersion. This level of environmental protection ensures reliable operation regardless of weather conditions or exposure to water during vehicle washing.
When examining vehicle camera aluminum shell vibration resistance on rough terrain, the maintenance of seal integrity under mechanical stress becomes particularly important. Aluminum's high stiffness prevents the housing deformation that can compromise seals in plastic housings subjected to continuous vibration. This characteristic makes aluminum the preferred choice for cameras mounted on vehicles that regularly operate on unpaved roads, construction sites, or other rough terrain where vibration is constant and severe.
Customization and Integration Possibilities
The manufacturing flexibility of aluminum enables camera housings that are precisely tailored to specific vehicle integration requirements. Advanced die-casting, extrusion, and machining processes can create complex geometries that optimize both internal component layout and external aerodynamic integration. This design freedom allows engineers to create housings that minimize wind noise, reduce drag, and maintain vehicle aesthetic appeal while providing optimal protection for the camera system.
Surface treatment options for aluminum further enhance integration possibilities. Anodizing processes can match housing color to vehicle trim, while specialized coatings can create specific optical properties around lens openings. The material compatibility with automotive paints and finishes ensures seamless visual integration with vehicle body panels, an important consideration for manufacturers focused on both function and form.
For those investigating lightweight aluminum casing for automotive camera durability, modern manufacturing techniques have expanded the possibilities for creating optimized housing designs. The development of thin-wall die casting and high-strength aluminum alloys has enabled lighter housings without compromising protection. Simultaneously, computer-aided engineering tools allow for precise optimization of material distribution, placing strength exactly where needed while eliminating unnecessary mass.
Long-Term Value and Reliability Considerations
Lifecycle Cost Analysis
While the initial manufacturing cost of aluminum camera housings may exceed that of plastic alternatives, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis often reveals significant long-term advantages. The extended service life, reduced failure rates, and maintained performance of aluminum-housed cameras frequently offset the initial investment through decreased warranty claims, reduced replacement costs, and maintained system functionality throughout the vehicle's lifespan.
The recyclability of aluminum further enhances its lifecycle value proposition. At end-of-life, aluminum housings can be completely recycled with minimal energy investment compared to primary production, contributing to circular economy principles in automotive manufacturing. This environmental consideration is increasingly important to both manufacturers and consumers focused on sustainability.
When evaluating total cost of ownership, the protective benefits of aluminum housings extend beyond the camera itself to the systems that depend on camera functionality. A failed camera in an advanced driver-assistance system may disable multiple safety features, creating potential liability and customer satisfaction issues that far exceed the cost difference between housing materials. This systems-level perspective demonstrates the value of investing in robust protection for critical automotive vision components.
Future-Proofing for Evolving Automotive Requirements
As vehicle capabilities continue advancing, camera systems face increasing demands for resolution, frame rate, and computational requirements. These advancements typically generate additional heat and require more sophisticated electronic components—factors that amplify the importance of effective thermal management and physical protection. Aluminum housings provide a foundation that can accommodate these evolving requirements without fundamental redesign, supporting higher-performance components within the same protective enclosure.
The material and manufacturing knowledge surrounding aluminum camera housings continues to advance alongside automotive requirements. New alloys with enhanced properties, improved surface treatments for specific environmental challenges, and advanced manufacturing techniques that reduce cost while improving performance all contribute to aluminum's ongoing suitability for next-generation vehicle cameras. This evolutionary path ensures that aluminum will remain a relevant and advantageous material choice as automotive vision systems continue their rapid development.
In conclusion, the selection of aluminum for vehicle camera housings represents a strategic engineering decision that addresses multiple challenges simultaneously. From thermal management to impact protection, corrosion resistance to electromagnetic shielding, aluminum provides a balanced combination of properties that ensure reliable camera performance under the demanding conditions encountered by modern vehicles. As automotive vision systems become increasingly critical to vehicle safety and functionality, the protective role of the camera housing becomes correspondingly important, making the choice of aluminum a investment in long-term performance and reliability.

 English
English 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch